DO YOU KNOW?
Our skin, being the largest organ on our body, is able to attain an absorption efficiency of 85% of negative ions, while we are only able to absorb 15% of negative ions through our respiratory system.
— Negatively Charged Electric Ion Treatment
NEORON® Fibre
Wearable Health’s concept lies in leveraging on the fact that our absorption efficiency of negative ions is highest via the skin, hence the fabrics we choose to wear can be a game-changer to our health. Moreover we are perpetually in clothing all day long. Why not choose clothing that is functional for your body’s well-being to help you achieve your health goals too?
Ultra Strong Negative Static & Negative Ions
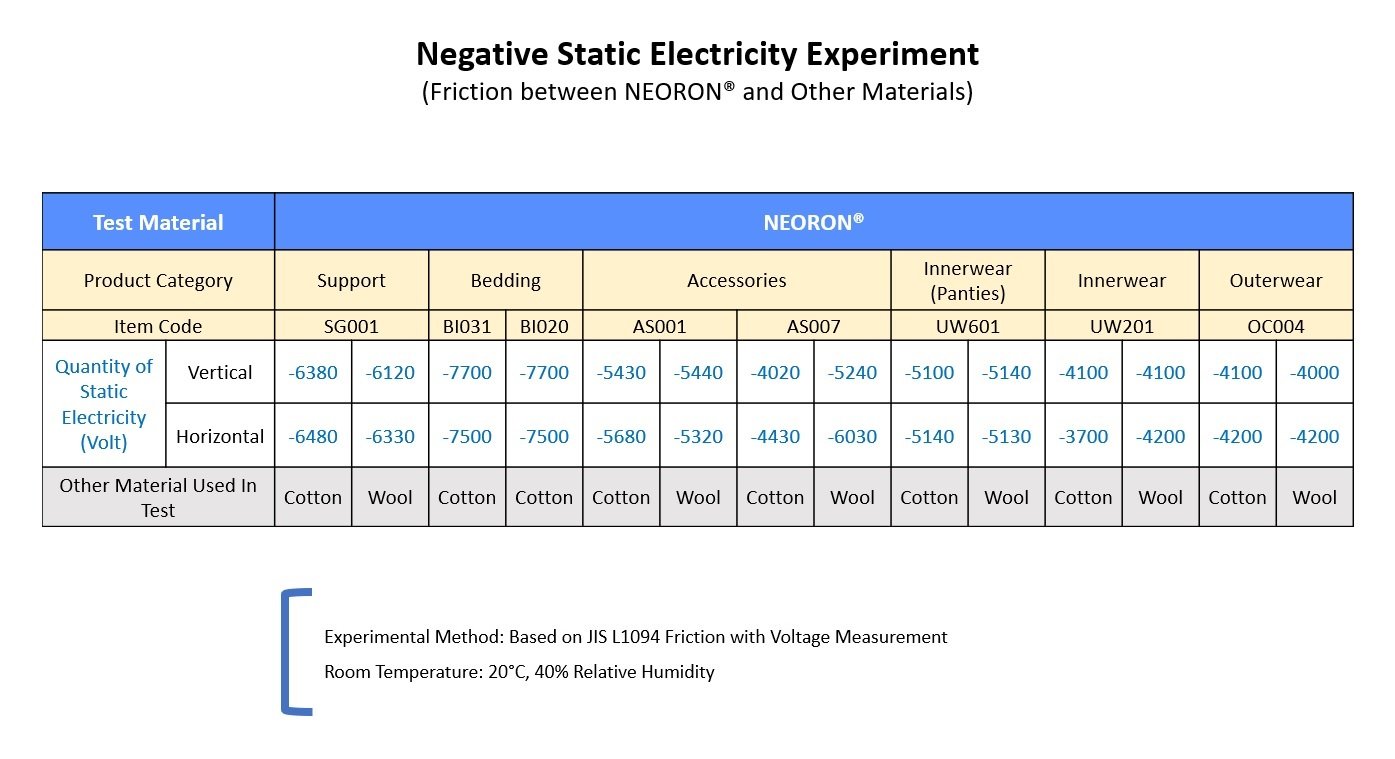
Through standardised tests and experiments conducted, NEORON® fibre has been proven to be capable of generating negative static electricity and negative ions through friction, by rubbing against the skin or other fibres.
Japan Textile Products Quality and Technology Center - JIS L1094:2014 Testing Methods for Electrostatic Propensity of Woven and Knitted Fabrics
Experiment - A NEORON® fibre test piece is attached to a rotating plate and a friction cloth (either cotton or wool) is positioned under the rotating plate. After that, the rotating plate is allowed to spin for 1 minute to generate friction between the two pieces of cloth.
The negative static electricity produced is measured, showing that NEORON® can produce a great amount of negative static electricity regardless whether it is rubbed against cotton or wool. The negative static electricity measured is between -3,000 and -3,200 volts. As a comparison, a Rayon sample is only able to generate -1,300 to -1,600 volts of negative static electricity.
Test piece dimension at 5cm by 8cm, environment temperature set at 20 degrees celcius and humidity level of 40%.
In general, all fibres produce an electric static charge when rubbed against another material.
According to the Japan Textile Industry Laboratory, fibre materials when rubbed against each other, may produce a negative or positive static charge relative to the material it is rubbed against. These major fibre samples are selected and charted out to show its tendency in static generation in comparison to another. TEVIRON, which is the predecessor technology of NEORON®, stays at the extreme end of the negative static charge, which means that users can be assured that TEVIRON/NEORON® fibre will consistently generate negative static charge regardless of the material it is rubbed against.
Samples of different negative ions clothing items made from NEORON® fibre were also tested. This chart shows that NEORON® fibre always produces negative static electricity regardless of the size or type of item.
It is advisable to speak to our consultants on user experience and how to discern if a particular item may have a stronger negative static propensity and negative ions count.
UNITIKA Garment Technology Co., Ltd. Research Laboratory Division
Experiment - A NEORON® fibre test piece is affixed on top of the tester and left for 1 minute, then rubbed for 30 seconds. These steps are repeated 3 times and the data recorded shows that the negative ions produced by the test cloth made from 100% NEORON® fibre was measured at an average of 3,471 negative ions/cc and a maximum average of 8,833 negative ions/cc. This means that NEORON® fibre can produce a great amount of negative ions through friction, particularly NEORON® cloth fabrics that are made from 100% NEORON® fibre.
Test piece dimension at 20cm by 20cm, environment temperature set at 20 degrees celcius and humidity level of 40%.
With ultra strong negative static and negative ions, our Wearable Health garments have added-on health functions, allowing direct skin contact facilitating better absorption of negative ions. Find out here what negative ions can do to improve our bodily functions.
Superior Moisture Permeability
NEORON® is a fibre that does not absorb water or perspiration. It dries quickly, keeping your skin dry, comfortable and warm.
Japan Textile Products Quality and Technology Center - JIS 1907 Testing Methods for Water Absorbency of Textiles (Byreck Method)
Experiment - Different fibre samples of the same length are put through a water absorption rate test. The fibre samples are fixed on a rod supported above a basin of dyed water and lowered to be immersed. After 10 minutes, the rod of fibre samples are removed and the rising height of the dyed water on each sample is measured.
From the test conducted, it shows that the water level of the NEORON® fibre sample did not exceed the starting line, which means that the water was not absorbed and hence did not travel upwards. In comparison with the other fibre samples, NEORON® fibre does not easily absorb water.
Test pieces dimension at 20cm by 2.5cm, starting line set 2cm from end of samples.
Cotton has always been a commonly worn fibre, especially in countries with all-year summer climate. However what is not widely known about Cotton is that its fibre structure allows retention of large amount of water. TEVIRON, the predecessor technology of NEORON® fibre, has however zero water absorption capabilities.
The implication of this difference is such that when we choose to wear fabrics made from cotton, thinking that we are able to feel cool from the summer temperatures, it may lead to perspiration being trapped within the cotton fibre structure for a long duration. When moisture comes into contact with our skin, not only does it start to encourage bacteria formation, our body reacts by giving off heat to “dry” the wet cotton fabric our skin is in direct contact with, causing a drop in body temperature, which then leads to a subsequent lowered immunity. This is even more so if the wet cotton fabric continues to be on our body under an air-conditioned environment.
A study from Carl Marx Textile Research Institute of Germany compared TEVIRON, the predecessor technology of NEORON® fibre, against other fibre samples such as Acrylic (commonly used to make Dri-Fit clothing) and Cotton in a liquid transfer rate experiment. It is found that TEVIRON/NEORON® fibre allows rapid water dispersion. This is also known as the “Sweat Dispersion Technology” when a material allows fast dispersion of perspiration or moisture out from the fibre structure, to be evaporated into the air. With such a feature, users wearing clothing made from TEVIRON/NEORON® fibre can be assured to feel dry at all times.
Teijin Limited Company of Japan, a century-long established chemical and pharmaceutical company, conducted an experiment where a specially designed clothing fabricated with one side made from cotton fibre, and another side made from NEORON® fibre, was worn on a subject while he exercised, thus inducing perspiration. It was found that Cotton took approximately 40 minutes to return to a dry state, whereas TEVIRON took only 10 minutes to be completely dry. This shows that TEVIRON/NEORON® fibre dries quickly, making washing and drying of our clothing a simpler and speedier task.
With superior moisture permeability, our Wearable Health garments allow you to feel dry at all times, especially when perspiration occurs in summer or in a country with an all-year summer climate. It prevents us from having a lowered body temperature & immunity and not fall sick easily. Its quick-dry function makes washing and drying our clothing an easier task.
Excellent Heat Insulation
NEORON® is a fibre with low heat conductivity. It has excellent heat insulation capabilities to prevent loss of body heat, keeping your body temperature consistent.
A common misunderstanding of clothing with heat insulation is that it should only be used at winter countries or cold weather. However it is important to know that regardless of the temperature of our external environment, it is vital to upkeep our body temperature at an optimal of 36.5 to 37 degrees celcius*. Hence, wearing clothing with heat insulation property helps to prevent loss of body heat, maintaining our natural body temperature for optimal functioning. It thereby also means that the fluctuations of the external environment does not easily affect our internal body temperature.
*source: <体温决定生老病死> “Body Temperature Determines Life & Death” - 石原结实博士 Dr Yumi Ishihara
Japan Textile Products Quality and Technology Center - JIS L 1096 Testing Methods for Warmth Retaining Property - Method A
Experiment - A warmth retaining tester is used and set at 36 degrees celcius and test cloths made from different fibres are placed on the radiating plate for a duration of 2 hours. The amount of electricity required to maintain each of the test cloths at 36 degrees celcius is recorded. A control experiment is also conducted whereby the amount of electricity required to maintain the radiating plate at 36 degrees celcius for a duration of 2 hours is recorded.
The difference in the amount of electricity required between the two tests (test cloth sample vs control experiment) is noted as the warmth retaining rate. The larger the difference, the better the warmth retaining rate.
Through the tests conducted, NEORON® has the highest warmth retaining rate of up to 34.6%. It is worth noting that Wool, a commonly used material to provide warmth, has only a warmth retaining rate of 29.8%. NEORON® fibre is highly effective in preventing the loss of body heat among other fibres.
Test sample pieces dimension at 30cm by 30cm.
UNITIKA Garment Technology Co., Ltd. Research Laboratory Division - Thermal Mannequin Test
Experiment - A thermal mannequin used to imitate the human body is set to a controlled temperature of 36 degrees celsius. Shirts made from Cotton and NEORON® fibre are put over the mannequin respectively and the testing time is set for an hour. A thermal imaging equipment is then used to capture the shirt’s surface after an hour.
The fabric that has good thermal insulation will indicate a lower surface temperature on the outside of the shirt, thus appearing as ‘blue’ on the imaging. The fabric with a poor thermal insulation will indicate a higher surface temperature on the outside of the shirt (ie. heat loss), thus appearing as ‘red’ on the imaging.
The results show that the shirt made from NEORON® fibre has a lower surface temperature of 30.6 degree celsius while the shirt made from Cotton has a higher surface temperature of 31.7 degree celsius. Therefore, NEORON® is a fibre that does not easily dissipate heat, keeping your body temperature consistent.
Test environment temperature set at 20 degrees celcius and humidity level of 65%.
Similar experiments were conducted to compare a selection of different materials of the same thickness to determine heat insulation capability. The experiments were conducted in varying temperatures of room temperature 25 degree celsius, 5 degree celsius and -5 degree celsius.
Experimental subjects were tasked to wrap different fibre materials in a controlled laboratory and the temperature difference is recorded between the side of the skin that is wrapped against the other that is unwrapped.
The results show consistently in both NEORON® fibre and its predecessor TEVIRON that they showed the highest temperature difference at -5 degree celsius, hence capable of providing the most warmth at a very cold temperature, making it an ideal wear for winter climates.
It is important to take note however, TEVIRON/NEORON® fibre was found to have similar skin temperature difference as typical clothing fibre such as Cotton, at a room temperature of 25 degree celsius, thus making it a clothing material that is also suitable for summer climates.
Conclusively, this would mean that TEVIRON/NEORON® fibre has a wide temperature range that can cater for warmth at cold temperatures, and feel cool on the skin like Cotton at hotter temperatures.
Experiment conducted by Journal of Occupation Health (Japan)
With excellent heat insulation property, our Wearable Health garments give you an added protection against heat loss, which may cause a subsequent lowered body temperature and lowered immunity. What’s more - it has a dual function to keep you warm at cold temperatures but cool at hotter temperatures, making it an exceptional and economic fabric to own and be ready for any season.
Outstanding Flame Retardancy
NEORON® fibre is a retardant material that is able to contain the spread of flames. NEORON® bedsheets and blankets are recognised as a fire prevention product by Japan Fire Retardant Association.
UNITIKA Garment Technology Co., Ltd. Research Laboratory Division - JIS L 1091 Testing Methods fo Flammability of Textiles - Method E
Experiment - Different fibre samples were cut at standard dimensions for a burning test to find out its Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) value, which is the minimum concentration of oxygen to support ignition and flaming combustion of the material. The higher the LOI, the more difficult it is to burn a particular material.
The oxygen concentration is adjusted for all test tubes in which the different fibre samples are ignited within. The LOI values are then determined based on the minimum oxygen level required for each test cloth samples to burn. If the LOI value is measured above 26, the fibre material is deemed to be flame retardant and will not burn easily.
Results show that NEORON® fibre has a LOI value of up to 36.8 which marks it as a fibre that is difficult to inflame. This proves that NEORON® fibre can effectively be used to prevent the spread of fire and is an extremely good flame-retardant & safe to use fibre material. Comparatively, Cotton which is a commonly used fibre material for homewear and bedding items, has a LOI value of only 18.9.
UNITIKA Garment Technology Co., Ltd. Research Laboratory Division - 45° Cigarette Method
Experiment - Four piece of Blanket and Bedsheet NEORON® fibre samples are cut at standard dimensions and prepared for this test. A lit cigarette is placed in between 2 stacks of 2 sample pieces each. The NEORON® cloths are then placed on a shelf with an inclination angle of 45° and ensured that there are no gaps between the test cloths and the lit cigarette. After an hour, the top two NEORON® cloths are removed to measure the carbonized area on each test cloths.
The results show that there is no flame remaining or any burning on the top and bottom NEORON® cloths. The flame did not spread towards the periphery of the test cloths. NEORON® fibre hence passed the 45° Cigarette Test that is based on the flame retardant product performance test standards set by the Japan Fire Retardant Association.
Test sample pieces dimension at 20cm by 15cm. NEORON® Blanket and Bedsheet sample pieces were used.
UNITIKA Garment Technology Co., Ltd. Research Laboratory Division - 45° Methenamine Method
Experiment - Different fibre samples are cut at standard dimensions and then placed on a shelf with an inclination angle of 45°. The test cloths are all ignited with a Methenamine tablet. The length of the carbonized area on each of the test cloths are then measured. The passing standards for this test to be deemed a fire retardant material have to be of an average length of 8cm or less, as set by the Japan Fire Retardant Association.
The results show that the average length of the carbonized area on the NEORON® test cloth is 4.7cm. However the Acrylic test cloth is completely burnt. This shows that Acrylic catches fire easily whereas NEORON® does not inflame easily even if fuel is used in ignition. NEORON® fibre hence passed the 45° Methenamine Method test that is based on the flame retardant product performance test standards set by the Japan Fire Retardant Association.
With NEORON® fibre passing both the 45° Cigarette Method and 45° Methenamine Method tests, the Japan Fire Retardant Association recognizes NEORON® Blankets and Bedsheets as flame-retardant products.
Test sample pieces dimension at 20cm by 15cm. NEORON® Blanket and Bedsheet sample pieces were used.